Hidden Desiccant
The Application of Polymer Desiccants in Implantable Medical Devices
Implantable medical devices refer to medical instruments implanted in patients through surgery for treatment, repair, replacement, or monitoring of physiological functions. Placed inside the body, these devices aim to improve the patient’s physiological condition, commonly used for long-term treatment or monitoring to enhance the quality of life or extend life.
These implantable medical devices require precise medical engineering and surgical techniques for design and use, coupled with regular monitoring and maintenance. The development of implantable medical devices has significantly improved the lives of many patients, offering effective treatment solutions for long-term chronic conditions.
Common implantable medical devices include:
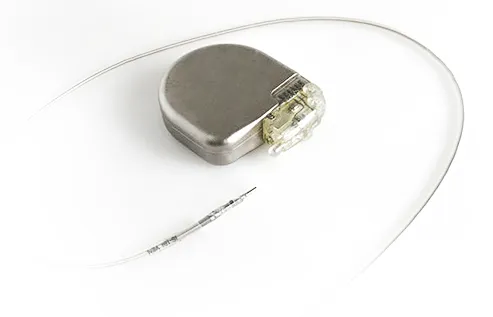
Pacemaker:
Controls the heart’s rhythm by sending electrical signals to maintain a normal heartbeat.

Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD):
Implantable Diabetes Treatment Devices

Exploring the Prolongation of Lifespan for Implantable Medical Devices

Moisture & Oxidation Protection
Controls the heart's rhythm by sending electrical signals to maintain a normal heartbeat.

Electronic Component Protection
Many implantable medical devices contain electronic components such as chips and sensors. These components are highly sensitive to humid environments, and thus, controlling humidity can reduce the risk of electronic component damage.
Traditional desiccants are often added to common medical devices to extend shelf life. Traditional desiccants, which use materials like silica gel and molecular sieves as absorbents, are delivered in small packet forms. However, such desiccants are not suitable for placement in precision instruments implanted in the human body due to the risk of packet rupture.




Not suitable for use in precision instruments implanted in the human body
Through close collaboration and research discussions with producers of implantable medical devices, WiseNano has discovered that polymer desiccants can effectively enhance the lifespan of these devices.
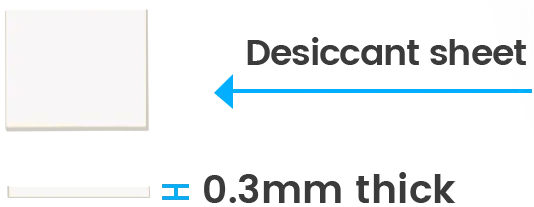
Polymer desiccants come in sheet and injection-molded forms
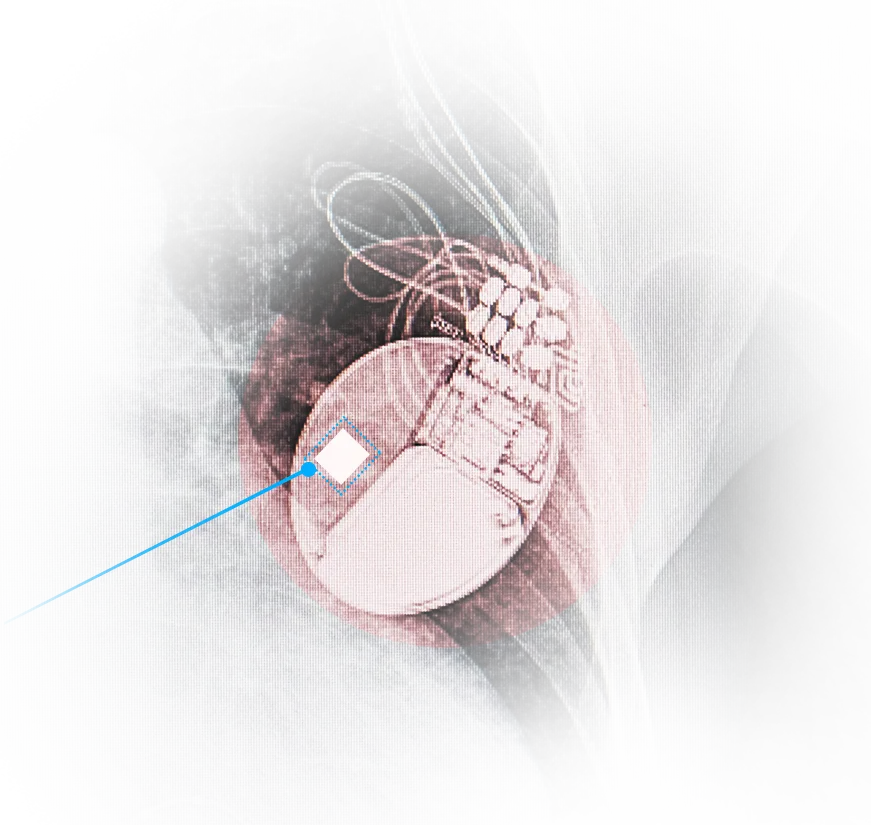
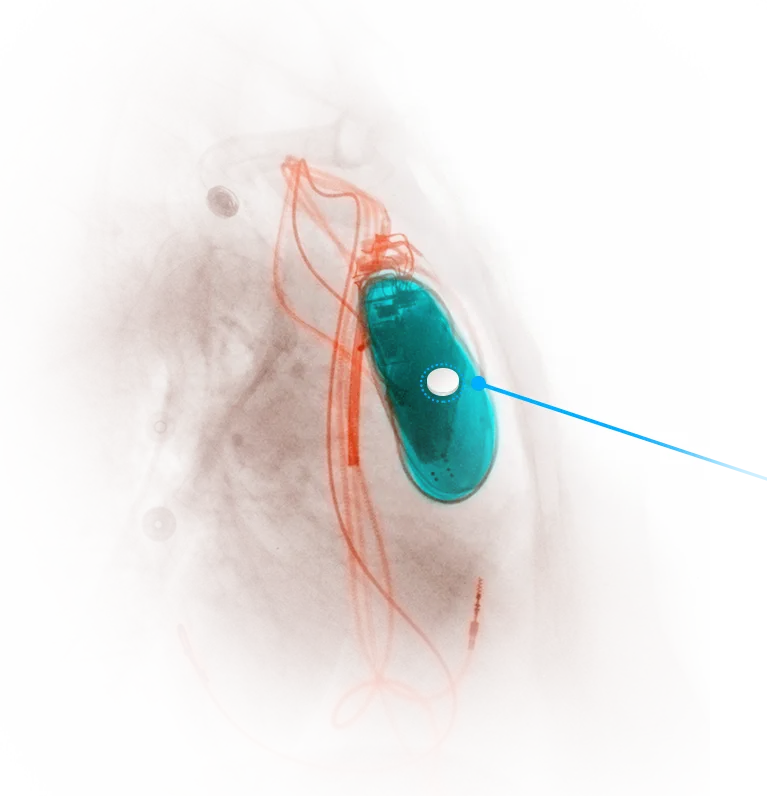
Desiccant sheets, 0.3mm thick, can be easily placed inside the shell of implantable medical devices without occupying excessive thickness or internal space. These sheets have inherent moisture-absorbing capabilities and pose no risk of packet rupture. WiseSheets with adhesive backing can be tailored into various shapes, adhering easily to the internal structure without easy detachment.